Cav2.1
Description: calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit Gene: Cacna1a Alias: ca2.1, EA2, FHM, MHP, rkr, APCA, HPCA, MHP1, SCA6, Caca1a, Cav2.1, Ccha1a, Cacnl1a4, Cacna1a
Cav2.1, encoded by the gene cacna1a, is a calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit . It is primarily expressed in the central nervous system and is responsible for controlling neurotransmitter release and neuronal excitability.
In humans, Cacna1a, the gene which encodes Cav2.1, is composed of 49 exons located on chromosome 19 at position 13. (19p13.13). [2427]
Like most Cav channels, Cacna1a is subject to alternative splicing. Seven exonic loci of the CaV2.1 gene have been shown to undergo alternative splicing
Some important exons, often involved in alternative splicing are:
| Species | NCBI accession | Length (nt) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | NM_000068.4 | 8660 | |
| Mouse | NM_007578.3 | 7929 | |
| Rat | NM_012918.4 | 8915 |
The human Cav2.1 protein is composed of 2506 amino acid (aa) and has a molecular weight of 282 Kda. The CACNA1A gene undergoes extensive alternative splicing, resulting in P/Q channels with different properties. These splice variants are differentially expressed throughout the CNS, and serve to adjust the biophysical parameters of the individual channel to correspond with its role in the various cell types. [2427]
For example, hippocampal synapses expressing Cav2.1 either with exon 47 (CaV2.1+47) or without (CaV2.1Δ47) differ in release probability and short-term plasticity [2428]. CaV2.1 channels that include exon EFb show calcium-dependent facilitation (CDF) only without exon 47 inclsuion, while CaV2.1 + EFa channels show robust CDF regardless of exon 47.
Expression of the variants and isoforms also differ between species. During development, rodent brains switch from high EFb to high EFa expression, but in humans, EFb and EFa expression is biphasic and varies with age and gender. EFa and EFb also show subcellular compartmentalization in neurons. [Ref]
Isoforms
To date there is no research on PTMS that affect Cav2.1
Like most Cav channels, Cav2.1 is made up of a single protein composed of 4 homologous domains (DI-DIV). Each domain is made up of 6 transmembrane subunits (S1-S6) connected by extracellular loops. S1-4 form the voltage sensing domain (VSD) whereas the S5-S6 act as the selectivity filter and form the pore module (PM). The S4 subunit of each domain contains a series of positively charged residues. The N-terminus and C-terminus of the α1 subunit have important roles in trafficking and anchoring of the subunit to the cell membrane. The C-terminus contains an Ile–Gln calmodulin-binding motif that helps to regulate calcium-dependent facilitation and inactivation of the channel.13 The intracellular loop between domains II and III of the α1 subunit contains a domain that can interact with G-protein-coupled receptors, as well as key motifs that interact with SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor) proteins, which are important for vesicular docking before exocytosis [2427]
The structure of Cav2.1 was resolved via electron-microscopy, giving us a detailed insight into the specific structural features the protein [2429] The overall structure of Cav2.1 closely resembles those of Cav2.2 and Cav2.3. The differences are mostly present in the extracellular loops in repeats I and IV, consistent with the sequence variations of these regions. This divergence in ECLs underlies the distinctive sensitivities of Cav2 channels to various peptide toxins [2429]
Cav2.1 predicted AlphaFold size
Methodology for AlphaFold size prediction and disclaimer are available here
Human CaV2.1 channels exhibit two distinct gating modes: slow and fast. In the slow mode, the channels have longer mean closed times and longer latency to first opening. Activation in the slow mode requires larger depolarizations, and inactivation kinetics are slower. Steady-state inactivation occurs at less negative voltages in the slow mode. Channels lacking a β subunit primarily operate in a low-po mode, which differs from both the slow and fast modes. In the low-po mode, the channels have shorter mean open times, longer mean closed times, longer first latency, a higher fraction of nulls, and activate at more positive voltages with a shallower voltage dependence. [2430]
Single channel unitary conductance
The single channel unitary conductance of Cav2.1 was measured between 9–19 pS. [2431] Single channel unitary conductance can change depending on experimental conditions and co-expressed subunits. The single channel unitary conductance of Cav2.1 is 19.5 pS for channels containing the β1b subunit, 20 pS for channels containing the β2e subunit, 19 pS for channels containing the β3a subunit, and 20 pS for channels containing the β4a subunit. [2430]
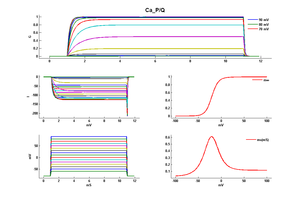
Model
Model Ca_P/Q (ID=5)
Junction potential corrected model
| Animal | rat | |
| CellType | Cerebellar Purkinje | |
| Age | 21 Days | |
| Temperature | 21.0°C | |
| Reversal | 135.0 mV | |
| Ion | Ca + | |
| Ligand ion | ||
| Reference | [261] T Miyasho et. al; Brain Res. 2001 Feb 9 | |
| mpower | 1.0 | |
| m Alpha | 8.5/(1+exp((v-8)/(-12.5))) | |
| m Beta | 35/(1+exp((v+74)/(14.5))) | |
The designation P/Q reflects the cell types from which its constituent currents were first isolated: the letter P is derived from Purkinje cells, and the letter Q refers to granule cells of the cerebellum where the channel is highly expressed. [2427]
Cav2.1 expression is almost exclusively restricted to neuronal and neuroendocrine (such as pituitary and pancreatic β) cells . The P/Q channel is widely expressed throughout the CNS but is particularly abundant in Purkinje and granule cells of the cerebellum [2427] but has also been identified in the cerebral cortex, thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus [2415]
Cav2.1 is predominantly localized at the presynaptic terminal, where they play a prominent role in controlling neurotransmitter release. They are also present at the somatodendritic membranes where they control certain postsynaptic events, such as neuronal excitability. [2432]
Within these locations, Cav2.1 exists in clusters of on average 18 channels [2433]
pivotal role in controlling neurotransmitter release from the pre-synaptic button and regulation of the firing behaviour through the integration of dendritic signals and generation of dendritic spikes. [2434] [2435] [2432]
The Cav2.1 channels also have indispensable roles in the postnatal development of the cerebellar circuitry. Cav2.1 fuels heterosynaptic competition between climbing and parallel fibers and also homosynaptic competition among multiple climbing fibers in developing cerebellum [2435]
Cav2.1 is also plays a calcium regulation role which contributes to the short term synaptic plasticity in certain neurons (hippocampal). Aberrant manipulation to the protein, particularly the CaM binding sites, lead to a reduction synaptic transmission facilitation and in turn a reduction in synaptic plasticity [2436] [2437]
Channelopathies
Given the importance of Cav2.1’s role in the brain, mutations to coding gene or protein are responsible for a number of pathologies
Familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 (FHM-1) is a Mendelian subtype of migraine with aura that is caused by missense mutations in the CACNA1A gene. FHM-1 mutation lead to gain-of-function of excitatory neurotransmission , including increased Cav2.1 current density in cerebellar neurons, enhanced neurotransmission at the neuromuscular junction, and, a reduced threshold and increased velocity of cortical spreading depression [2432]
Mutation to Cav2.1 are also responsible for different types of Ataxia: Spinocerebellar Ataxia type 6 (SCA6) and Episodic Ataxia type 2 (EA2) [2438].
- SCA6 results from an expansion of ‘CAG’ polyglutamine repeats in COOH tail of CACNA1A protein. This results in a toxic gain-of-function affecting channel regulation leading to the selective degeneration of cerebellar Purkinje cells (8988170)
- SCA2 results from loss-of-function mutations leading to decreased channel function and thereby a decrease in intracellular Ca 2+
Other mutation to CACNA1A gene are responsible for certain types of epileptic encephalopathies (EEs) [2439]
On top of causing own set of diseases, changes to Cav1.2 also accompany other diseases. Most cases with CACNA1A variants present with ataxia, epilepsy, attention deficit hyperactive disorder, autism spectrum disorder, dysmorphic features and eye abnormalities such as nystagmus, paroxysmal tonic upgaze, dysmetric saccades, blindness, myoclonus, ocular apraxia, exophthalmos and bilateral esotropia. Schizophrenia, anxiety, depression, hemiplegic migraine, coma, conductive deafness, vertigo attacks, dysarthria, tremors, athetosis, optic nerve glioma, abnormal behaviors such as aggression, sleeping problems can also be noticed. [2415] Cav2.1 is also regularly under-expressed in certain cancers, such as the brain or breast [2440]
Auxiliary subunit
Cav2.1 channels typically exist as multi-subunit complexes comprised of the main pore-forming α1 subunit, as previously described, and auxiliary subunits α2δ-2, β2 subunits [2373] The β and α2δ auxiliary subunits coassemble with the α1 subunit in a 1:1:1 stoichiometric ratio and influence both trafficking and kinetic properties of the pore-forming subunits [2441] [2427] Four different α2δ subunits have been described (α2δ-1 to α2δ-4), which may interact with Cav2.1 at different degrees of association [2441] Four Cav-β subunits (β1b, β2e, β3a, or β4a) have been identified differentially expressed in neurons and are able to interact with Cav2.1. The type of β subunit modulates the occurrence of these modes and their inactivation properties. As all four subunits can act on Cav2.1 simultaneously, which combination of β subunits interactions occur will also influence the final properties the channel. Without β subunits, CaV2.1 channels show shorter open times, longer closed times, longer first latency, more nulls, and require higher voltage for activation. [2430]
Calcium & CaM
Cav2.1 allows the passage of Ca2+ ions in and out of the cell. However, it is itself sensitive to the fluctuation concentrations of the ion and can undergo Ca2+ dependent inactivation thanks to its interaction with certain proteins, namely CAM. [2442] Binding of CaM occurs at the C-terminus, which contains an Ile–Gln calmodulin-binding. [2427]
It is though that Ca(2+)-free CaM, apoCaM may "pre-associate" with these Cav2.1 to enhance detection of local Ca(2+). [2443]
Other Proteins
The intracellular loops of Cav2.1, between domains II and III, t contains a domain that can interact with G-protein-coupled receptors, as well as key motifs that interact with SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor) proteins. G protein coupled receptors are established to orchestrate precise regulation of neurotransmitters and hormone release through inhibition of CaV2 channels. SNARE proteins are important for vesicular docking before exocytosis [2427] [476]
RIM-binding proteins (RIM-BPs) are multidomain active zone proteins that bind to RIMs and to Ca(2+) channels. RIM-BPs are not essential for neurotransmitter release, but are required for high-fidelity coupling of action potential-induced Ca(2+) influx to Ca(2+)-stimulated synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Deletion of RIM-BPs decelerated action-potential-triggered neurotransmitter release and rendered it unreliable, thereby impairing the fidelity of synaptic transmission. [2444]
Bassoon is a presynaptic scaffolding protein Bassoon localized specifically to active zones, similarly ot Cav2.1, at the active zone (CAZ) where neurotransmitter is released- This is done via molecular interaction with the RIM-binding proteins (RBPs). A genetic deletion of Bassoon or interference with Bassoon-RBP interaction reduces synaptic numbers of CaV2.1 and weakens P/Q-type Ca(2+) current-driven synaptic transmission [2434]
Laminin beta2 is a component of the synaptic cleft at the neuromuscular junction. Laminin beta2 binds directly to calcium channels, including Cav2.1, that are required for neurotransmitter release from motor nerve terminals. This interaction leads to clustering of channels, which in turn recruits other presynaptic components. Perturbation of this interaction in vivo results in disassembly of neurotransmitter release sites [2445]
Large-conductance calcium- and voltage-activated potassium channels (BKCa) are activated by both membrane depolarization and elevation of cytosolic calcium ions (Ca2+). Under physiological conditions, BKCa channel activation requires Ca2+ concentrations that typically occur in close proximity to Ca2+ sources. Based on this knowledge, BKCa channels were shown to assemble into macromolecular complexes with the voltage-gated calcium channels including, Cav1.2 (L-type), Cav2.1 (P/Q-type), and Cav2.2 (N-type). [2446]
Nrxns are polymorphic synaptic cell adhesion molecules, for which multiple presynaptic and postsynaptic ligands exist. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings show that Nrxn1α in combination with α2δ-1, but not with α2δ-3, facilitates Ca2+ currents of recombinant CaV2.1 without altering channel kinetics. Though not acting directly of Cav2.1 presynaptic Nrxn1α does act as a positive regulator of Ca2+ influx through CaV2.1 channels containing α2δ-1 subunits [2441]
Cav2.1 has a high sensitivity to the funnel web spider venom Omega-agatoxin-IVA. [555]
Roscovitine, a potent inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases 1, 2, and 5, slows the deactivation of P/Q (Cav2.2) and N-type (CaV2.1) calcium channels. [93]
References
Miki T
et al.
Two novel alleles of tottering with distinct Ca(v)2.1 calcium channel neuropathologies.
Neuroscience,
2008
Jul
31
, 155 (31-44).
Chen H
et al.
Altered frequency-dependent inactivation and steady-state inactivation of polyglutamine-expanded alpha1A in SCA6.
Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol.,
2007
Mar
, 292 (C1078-86).
Tanaka K
et al.
Increased Ca2+ channel currents in cerebellar Purkinje cells of the ataxic groggy rat.
Neurosci. Lett.,
2007
Oct
16
, 426 (75-80).
Tsunemi T
et al.
Novel Cav2.1 splice variants isolated from Purkinje cells do not generate P-type Ca2+ current.
J. Biol. Chem.,
2002
Mar
1
, 277 (7214-21).
Hans M
et al.
Structural elements in domain IV that influence biophysical and pharmacological properties of human alpha1A-containing high-voltage-activated calcium channels.
Biophys. J.,
1999
Mar
, 76 (1384-400).
Serra SA
et al.
The hemiplegic migraine-associated Y1245C mutation in CACNA1A results in a gain of channel function due to its effect on the voltage sensor and G-protein-mediated inhibition.
Pflugers Arch.,
2009
Jul
, 458 (489-502).
Buraei Z
et al.
Slowed N-type calcium channel (CaV2.2) deactivation by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor roscovitine.
Biophys. J.,
2005
Sep
, 89 (1681-91).
Li L
et al.
Differential gating and recruitment of P/Q-, N-, and R-type Ca2+ channels in hippocampal mossy fiber boutons.
J. Neurosci.,
2007
Dec
5
, 27 (13420-9).
Dolphin AC
Calcium channel diversity: multiple roles of calcium channel subunits.
Curr. Opin. Neurobiol.,
2009
Jun
, 19 (237-44).
Miyasho T
et al.
Low-threshold potassium channels and a low-threshold calcium channel regulate Ca2+ spike firing in the dendrites of cerebellar Purkinje neurons: a modeling study.
Brain Res.,
2001
Feb
9
, 891 (106-15).
Llinás R
et al.
Distribution and functional significance of the P-type, voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in the mammalian central nervous system.
Trends Neurosci.,
1992
Sep
, 15 (351-5).
Mintz IM
et al.
P-type calcium channels in rat central and peripheral neurons.
Neuron,
1992
Jul
, 9 (85-95).
Sutton KG
et al.
P/Q-type calcium channels mediate the activity-dependent feedback of syntaxin-1A.
Nature,
1999
Oct
21
, 401 (800-4).
Ludwig A
et al.
Regional expression and cellular localization of the alpha1 and beta subunit of high voltage-activated calcium channels in rat brain.
J. Neurosci.,
1997
Feb
15
, 17 (1339-49).
Starr TV
et al.
Primary structure of a calcium channel that is highly expressed in the rat cerebellum.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,
1991
Jul
1
, 88 (5621-5).
Currie KP
G protein modulation of CaV2 voltage-gated calcium channels.
Channels (Austin),
2010 Nov-Dec
, 4 (497-509).
Mintz IM
et al.
Block of calcium channels in rat neurons by synthetic omega-Aga-IVA.
Neuropharmacology,
1993
Nov
, 32 (1161-9).
Hofmann F
et al.
L-type CaV1.2 calcium channels: from in vitro findings to in vivo function.
Physiol. Rev.,
2014
Jan
, 94 (303-26).
Kessi M
et al.
Calcium channelopathies and intellectual disability: a systematic review.
Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2021May13, 16 (219).
Rajakulendran S
et al.
Neuronal P/Q-type calcium channel dysfunction in inherited disorders of the CNS.
,
2012
Jan
17
, ().
Heck J
et al.
Transient Confinement of CaV2.1 Ca2+-Channel Splice Variants Shapes Synaptic Short-Term Plasticity.
Neuron, 2019Jul03, 103 (66-79.e12).
Li Z
et al.
Structural basis for different ω-agatoxin IVA sensitivities of the P-type and Q-type Cav2.1 channels.
Cell Res, 2024Jun, 34 (455-457).
Luvisetto S
et al.
Modal gating of human CaV2.1 (P/Q-type) calcium channels: I. The slow and the fast gating modes and their modulation by beta subunits.
J. Gen. Physiol.,
2004
Nov
, 124 (445-61).
Sheng J
et al.
Calcium-channel number critically influences synaptic strength and plasticity at the active zone.
Nat. Neurosci.,
2012
Jul
, 15 (998-1006).
Van Den Maagdenberg AM
et al.
A Cacna1a knockin migraine mouse model with increased susceptibility to cortical spreading depression.
Neuron,
2004
Mar
4
, 41 (701-10).
Nakamura Y
et al.
Nanoscale distribution of presynaptic Ca(2+) channels and its impact on vesicular release during development.
Neuron,
2015
Jan
7
, 85 (145-58).
Davydova D
et al.
Bassoon specifically controls presynaptic P/Q-type Ca(2+) channels via RIM-binding protein.
Neuron,
2014
Apr
2
, 82 (181-94).
Indriati DW
et al.
Quantitative localization of Cav2.1 (P/Q-type) voltage-dependent calcium channels in Purkinje cells: somatodendritic gradient and distinct somatic coclustering with calcium-activated potassium channels.
J. Neurosci.,
2013
Feb
20
, 33 (3668-78).
Mochida S
et al.
Regulation of presynaptic Ca(V)2.1 channels by Ca2+ sensor proteins mediates short-term synaptic plasticity.
Neuron,
2008
Jan
24
, 57 (210-6).
Nanou E
et al.
Calcium sensor regulation of the CaV2.1 Ca2+ channel contributes to short-term synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,
2016
Jan
26
, 113 (1062-7).
De Novo Mutations in SLC1A2 and CACNA1A Are Important Causes of Epileptic Encephalopathies.
Am J Hum Genet, 2016Aug04, 99 (287-98).
Phan NN
et al.
Voltage-gated calcium channels: Novel targets for cancer therapy.
Oncol Lett, 2017Aug, 14 (2059-2074).
Brockhaus J
et al.
α-Neurexins Together with α2δ-1 Auxiliary Subunits Regulate Ca2+ Influx through Cav2.1 Channels.
J Neurosci, 2018Sep19, 38 (8277-8294).
Peterson BZ
et al.
Calmodulin is the Ca2+ sensor for Ca2+ -dependent inactivation of L-type calcium channels.
Neuron,
1999
Mar
, 22 (549-58).
Erickson MG
et al.
Preassociation of calmodulin with voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels revealed by FRET in single living cells.
Neuron,
2001
Sep
27
, 31 (973-85).
Acuna C
et al.
RIM-BPs Mediate Tight Coupling of Action Potentials to Ca(2+)-Triggered Neurotransmitter Release.
Neuron,
2015
Sep
23
, 87 (1234-47).
Nishimune H
et al.
A synaptic laminin-calcium channel interaction organizes active zones in motor nerve terminals.
Nature,
2004
Dec
2
, 432 (580-7).
Berkefeld H
et al.
BKCa-Cav channel complexes mediate rapid and localized Ca2+-activated K+ signaling.
Science,
2006
Oct
27
, 314 (615-20).
Contributors: Katherine Johnston, Rajnish Ranjan, Michael Schartner
To cite this page: [Contributors] Channelpedia https://channelpedia.epfl.ch/wikipages/78/ , accessed on 2026 Feb 23