Cav2.2
Description: calcium channel, voltage-dependent, N type, alpha 1B subunit Gene: Cacna1b Alias: ca2.2, BIII, CACNN, Cav2.2, CACNL1A5, CACNA1B
Cav2.2, encoded by the gene Cacna1b is calcium, voltage-gated, N type, alpha subunit channel. Cav2.2 is predominantly expressed in nociceptive neurons. It is involved in the generation of the N-type current and entry of Ca2+ which controls neurotransmitter release
In humans, cacna1b, the gene which encodes Cav2.2, is composed of 47 exons located on chromosome 9 at position 34. (9q34.3). [2427]
Like most Cav channels, the coding gene of Cav2.2, Cacna1b, is subject to alternative splicing.
One important exon, often involved in alternative splicing, is Exon 37. Exons 37a and 37b are a pair of mutually exclusive exons encoding two alternative 32–amino acid modules (e37a and e37b, respectively) at the C terminus of CaV2.2. CaV2.2 e37a, is notable for its enrichment in nociceptors. [2447] [2448]
| Species | NCBI accession | Length (nt) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | NM_000718.4 | 9792 | |
| Mouse | NM_001042528.2 | 9772 | |
| Rat | NM_001195199.1 | 7065 |
The human Cav2.2 protein is composed of 2339 amino acid (aa) and has a molecular weight of 262 Kda. The CACNA1B gene undergoes extensive alternative splicing, resulting in Cav2.2 channels with different properties. These serve to adjust the biophysical parameters of the individual channel to correspond with its role in the various cell types.
Of the 32 amino acids coded for by the exon 37a or 37b, 14 of them differ between. CaV2.2 e37a]mRNAs are enriched in nociceptors of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and expressed at lower levels in other regions including the brain, while CaV2.2 e37b mRNAs are ubiquitous in the nervous system. Substitution of e37b with e37a increases CaV2.2 current densities and consequently calcium entry during action-potential waveforms [2447] [2449] [2448]
Isoforms
Like most mammalian proteins, Cav2.2 is subject to post translational modifications (PTM).
It was demonstrated that Cav2.2 can be phosphorylated. This is conducted by a number of kinases including Cdk5, protein kinases A and C, PKA and PKC.
CdK5 phosphorylation increases calcium influx by enhancing channel open probability, in turn facilitating neurotransmitter release. [2450] PKA- and PKC-mediated phosphorylation both inhibit CaV2.2 interaction with SNARE complexes In addition, PKC-mediated phosphorylation also enhances N-type calcium current by reducing the G-protein inhibition of CaV2.2. Furthermore, PKC phosphorylation in the I–II linker region reduces the inhibitory effect of the Gβγ subunits on CaV2.2 [2451]
Like most Cav channels, Cav2.2 is made up of a single protein composed of 4 homologous domains (DI-DIV). Each domain is made up of 6 transmembrane subunits (S1-S6) connected by extracellular loops. S1-4 form the voltage sensing domain (VSD) whereas the S5-S6 act as the selectivity filter and form the pore module (PM). The S4 subunit of each domain contains a series of positively charged residues. The N-terminus and C-terminus of the α1 subunit have important roles in trafficking and anchoring of the subunit to the cell membrane. The intracellular loop between domains II and III of the α1 subunit contains a domain that can interact with G-protein-coupled receptors, as well as key motifs that interact with SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor) proteins, which are important for vesicular docking before exocytosis [2451] [2452]
The structure of human Cav2.2 was resolved via cryo-electron microscopy to an overall resolution of 3.1 angstroms, giving us a detailed insight to the channel’s architecture. Structural resolution of the ion channel highlighted a number of Cav2.2 specific features [2451] [2452] :
- A unique VSDII, stabilized in a 'down' conformation by specific Cav2 interactions, including a bound phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) molecule
- A S6 helix extension, reaching further into the cytoplasm than that in Cav1 and Cav3 families. The segment contributes to stabilizing the closed state of the pore by interacting with other structural elements, namely close contact with the β1 subunit, potentially also affecting gate regulation
- Cav2.2 contains a signature EEEE motif (Glu314, Glu663, Glu1365, and Glu1655) that coordinates a Ca²⁺ ion at the selectivity filter's outer site
- The S1–S2 loops of VSDII interact similarly with the α2δ1 subunit as in Cav1.1, indicating conserved binding geometry.
- Specific α Helix that locks the intracellular gate in the closed conformation, contributing to the rapid inactivation of Cav2.2 during repolarization
- The intracellular domain between the II–III loops of the CaV2.2 is known as the synaptic protein interaction (synprint) region. This area plays key role in neurotransmitter release and directly binds with several important synaptic transmission proteins.
Cav2.2 predicted AlphaFold size
Methodology for AlphaFold size prediction and disclaimer are available here
Cav2.2 are known to be fast- activated and high-voltage-activated and conduct N-type Cav current. (16267232)
The biophysical properties of N-type current falls between T- and L-type Cav currents as it displays smaller unitary Ba2+ conductance, lower activation threshold, and faster inactivation rate than L-type Cav currents, but larger unitary Ba2+ conductance, higher activation threshold, and slower inactivation rate than T-type CaV currents [2453] [477]
Single channel unitary conductance
The single channel unitary conductance of Cav2.1 is estimated at 16.8 ± 1.2 pS. [2454]
Model
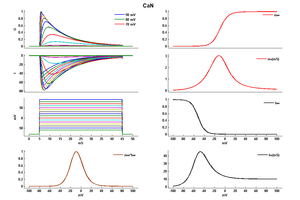
Model CaN (ID=6)
| Animal | Cat | |
| CellType | RGC | |
| Age | 34 Days | |
| Temperature | 36.0°C | |
| Reversal | 135.0 mV | |
| Ion | Ca + | |
| Ligand ion | ||
| Reference | [259] S J Huang et. al; Neuroscience 1998 Jul | |
| mpower | 2.0 | |
| m Alpha | (0.1*(v-20)/(1-exp(-(v-20)/10))) If v neq 20 | |
| m Beta | 0.4*exp(-(v+25)/18) | |
| hpower | 1.0 | |
| h Alpha | 0.01*exp(-(v+50)/10) | |
| h Beta | 0.1/(1+exp(-(v+17)/17)) | |
Cav2.2 is located in the brain and is the peripheral nervous system, notably in the spinal cord and primary sensory neurons. [2440] [2447]
Cav2.2 channels are predominantly located at the presynaptic terminal of nociceptive neurons but they can also be found at the soma. [2447] [2455]
Cav2.2 channels are responsible for the entry of Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminal and mediate key events including synaptogenesis and neurotransmission . [2455]
Given their predominant expression location in nociceptive neurons, they play a pivotal role in the control release of neurotransmitters and the transmission of nociceptive signaling . Further evidence of this nociceptor role comes from KO mice models. Mice lacking the CaV2.2 subunit have higher pain thresholds compared to wild-type [2448]
Cav2.2 plays an essential role as a scaffolding protein in the organizing of the presynaptic terminal zones. Double knock-out mice for Cav2.1 and Cav2.2 result a reduced number of normal sized active zones, along with docked vesicles and fewer active zone proteins Bassoon, Piccolo, and CAST/Erc2 [2456]
Channelopathies
Interestingly, very few channelopathies have been associated with mutations to CACNA1B.
Cav2.2 is needed to ensure transmission of nociceptive information, through neuronal firing and neurotransmitter release[2440]. Deletion or aberration of Cav2.2, would lead a loss of this signal. Indeed, KO mouse models show that have higher pain thresholds compared to wild type[2448] . Therefore Cav2.2, though not responsible for neuropathic pain, could serve as a target for pain treatment /management [2457]
The first congenital mutation in Cav2.2 associated with a pathology was myoclonus-dystonia-like syndrome, identified in 2015. Myoclonus-dystonia (M-D) is a movement disorder that typically affects the upper half of the body characterised by quick, involuntary muscle jerking or twitching (myo-clonus) and can be, in some cases, accompanied by psychological symptoms such as obsessive-compulsive disorders, anxiety and depression. (26218636). The identified mutation results in a substitution in the pore-forming loop between Domain 3 S5-S6, essential for proper calcium conductivity. (26218636)
Other Cav2.2 mutations were also identified through GWS. These aberrations were associated with other pathologies but are not directly the cause for them. Associated pathologies include bipolar disorder [2458], schizophrenia [2459], and autism [2460].
Auxiliary subunit
Cav2.1 channels typically exist as multi-subunit complexes composed of the main pore-forming α1 subunit, as previously described, and auxiliary subunits α2δ-, β-subunits.
- Many studies have indicated that α2δ-subunits are important for the correct trafficking and physiological function of the channels.[2461] α2δ subunits modulate calcium channel current kinetics and also increase trafficking of the channel to the plasma membrane [2462] Genetic ablation of α2δ-1 leads to both a drop in Cav2.2 cell surface expression and lower calcium current densities [2461] [2463]
- Beta 3 Subunit: Overexpressed beta 3 subunit (12.5 ng/cell cRNA) significantly suppressed N- and R-type, but not L-type calcium channel currents at holding potentials of 60 and 80 mV.[92]
CaM & CDI
Cav2.2 allows the passage of Ca2+ ions in and out of the cell. However, it is itself sensitive to the fluctuation concentrations of the ion and can undergo Ca2+ dependent inactivation thanks to its interaction with certain proteins, namely CaM. Cav2.2 CDI manifests itself by accelerated decay of Ca2+ current [2389]
G protein inhibition
The most widespread form of Cav2.2 inhibition is by G protein-coupled receptors. G protein-coupled receptor inhibition of these channels is typically voltage-dependent and mediated by Gβγ [2447] This form of inhibition is fast, membrane specific and voltage-dependent. It is thought to play a key role in control of transmitter release and is especially effective at attenuating low-frequency stimuli [2447]
Other proteins
Cav2.2 channels interact directly with the SNARE proteins and synaptotagmin through a specific synaptic protein interaction (synprint) site in the large intracellular loop connecting domains II and III. This interaction is regulated by Ca2+ and by protein phosphorylation. [477] The synprint region of CaV2.2 is also a binding site for the active zone protein RIM1. RIM1 can interact with the β auxiliary subunit of P/Q-type calcium channels to suppress inactivation, allow calcium influx, and facilitate synaptic vesicle docking to the active zone. Furthermore, RIM1 directly binds the C-terminal regions of the α1 subunit of both N- and P/Q-type calcium channels, and it tethers these channels to presynaptic terminals in order to facilitate synchronous transmitter release [2451]
Large-conductance calcium- and voltage-activated potassium channels (BKCa) are activated by both membrane depolarization and elevation of cytosolic calcium ions (Ca2+). Under physiological conditions, BKCa channel activation requires Ca2+ concentrations that typically occur in close proximity to Ca2+ sources. Based on this knowledge, BKCa channels were shown to assemble into macromolecular complexes with the voltage-gated calcium channels including, Cav1.2 (L-type), Cav2.1 (P/Q-type), and Cav2.2 (N-type). [2446]
Neurokinin 1 Receptor: unlike R-type channels encoded by CaV2.3, L-type (CaV1.3), N-type (CaV2.2), and P/Q-type (CaV2.1) channels are inhibited, but not stimulated, through Neurokinin 1 receptors. [89]
Roscovitine, a potent inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases 1, 2, and 5, slows the deactivation of P/Q (Cav2.1) and N-type (Cav2.2) calcium channels. [93]
References
Page KM
et al.
N terminus is key to the dominant negative suppression of Ca(V)2 calcium channels: implications for episodic ataxia type 2.
J. Biol. Chem.,
2010
Jan
8
, 285 (835-44).
Meza U
et al.
Neurokinin 1 receptors trigger overlapping stimulation and inhibition of CaV2.3 (R-type) calcium channels.
Mol. Pharmacol.,
2007
Jan
, 71 (284-93).
Vitko I
et al.
Orientation of the calcium channel beta relative to the alpha(1)2.2 subunit is critical for its regulation of channel activity.
PLoS ONE,
2008
, 3 (e3560).
Yasuda T
et al.
Overexpressed Ca(v)beta3 inhibits N-type (Cav2.2) calcium channel currents through a hyperpolarizing shift of ultra-slow and closed-state inactivation.
J. Gen. Physiol.,
2004
Apr
, 123 (401-16).
Buraei Z
et al.
Slowed N-type calcium channel (CaV2.2) deactivation by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor roscovitine.
Biophys. J.,
2005
Sep
, 89 (1681-91).
Leroy J
et al.
Interaction via a key tryptophan in the I-II linker of N-type calcium channels is required for beta1 but not for palmitoylated beta2, implicating an additional binding site in the regulation of channel voltage-dependent properties.
J. Neurosci.,
2005
Jul
27
, 25 (6984-96).
Helton TD
et al.
Neuronal L-type calcium channels open quickly and are inhibited slowly.
J. Neurosci.,
2005
Nov
2
, 25 (10247-51).
Raghib A
et al.
Dominant-negative synthesis suppression of voltage-gated calcium channel Cav2.2 induced by truncated constructs.
J. Neurosci.,
2001
Nov
1
, 21 (8495-504).
Li L
et al.
Differential gating and recruitment of P/Q-, N-, and R-type Ca2+ channels in hippocampal mossy fiber boutons.
J. Neurosci.,
2007
Dec
5
, 27 (13420-9).
Huang SJ
et al.
Activation and inactivation properties of voltage-gated calcium currents in developing cat retinal ganglion cells.
Neuroscience,
1998
Jul
, 85 (239-47).
Benison G
et al.
Modeling temporal behavior of postnatal cat retinal ganglion cells.
J. Theor. Biol.,
2001
May
21
, 210 (187-99).
Catterall WA
Structure and regulation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.
Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol.,
2000
, 16 (521-55).
Black JL
The voltage-gated calcium channel gamma subunits: a review of the literature.
J. Bioenerg. Biomembr.,
2003
Dec
, 35 (649-60).
Mintz IM
et al.
Block of calcium channels in rat neurons by synthetic omega-Aga-IVA.
Neuropharmacology,
1993
Nov
, 32 (1161-9).
Dick IE
et al.
A modular switch for spatial Ca2+ selectivity in the calmodulin regulation of CaV channels.
Nature,
2008
Feb
14
, 451 (830-4).
Rajakulendran S
et al.
Neuronal P/Q-type calcium channel dysfunction in inherited disorders of the CNS.
,
2012
Jan
17
, ().
Phan NN
et al.
Voltage-gated calcium channels: Novel targets for cancer therapy.
Oncol Lett, 2017Aug, 14 (2059-2074).
Berkefeld H
et al.
BKCa-Cav channel complexes mediate rapid and localized Ca2+-activated K+ signaling.
Science,
2006
Oct
27
, 314 (615-20).
Raingo J
et al.
Alternative splicing controls G protein-dependent inhibition of N-type calcium channels in nociceptors.
Nat. Neurosci.,
2007
Mar
, 10 (285-92).
Bell TJ
et al.
Cell-specific alternative splicing increases calcium channel current density in the pain pathway.
Neuron,
2004
Jan
8
, 41 (127-38).
Andrade A
et al.
Opioid inhibition of N-type Ca2+ channels and spinal analgesia couple to alternative splicing.
Nat. Neurosci.,
2010
Oct
, 13 (1249-56).
Kim SH
et al.
Balance of calcineurin Aα and CDK5 activities sets release probability at nerve terminals.
J Neurosci, 2013May22, 33 (8937-50).
Su SC
et al.
Regulation of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels and presynaptic function by cyclin-dependent kinase 5.
Neuron,
2012
Aug
23
, 75 (675-87).
Gao S
et al.
Structure of human Cav2.2 channel blocked by the painkiller ziconotide.
Nature, 2021Aug, 596 (143-147).
Yang SN
et al.
The role of voltage-gated calcium channels in pancreatic beta-cell physiology and pathophysiology.
Endocr. Rev.,
2006
Oct
, 27 (621-76).
Maingret F
et al.
Neurotransmitter modulation of small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels by regulation of Ca2+ gating.
Neuron,
2008
Aug
14
, 59 (439-49).
DuBreuil DM
et al.
Heat But Not Mechanical Hypersensitivity Depends on Voltage-Gated CaV2.2 Calcium Channel Activity in Peripheral Axon Terminals Innervating Skin.
J Neurosci, 2021Sep08, 41 (7546-7560).
Chen J
et al.
Calcium channels link the muscle-derived synapse organizer laminin β2 to Bassoon and CAST/Erc2 to organize presynaptic active zones.
J. Neurosci.,
2011
Jan
12
, 31 (512-25).
Tibbs GR
et al.
Voltage-Gated Ion Channels in the PNS: Novel Therapies for Neuropathic Pain?
Trends Pharmacol. Sci.,
2016
May
24
, ().
Ament SA
et al.
Rare variants in neuronal excitability genes influence risk for bipolar disorder.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,
2015
Mar
17
, 112 (3576-81).
Glessner JT
et al.
Strong synaptic transmission impact by copy number variations in schizophrenia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010Jun08, 107 (10584-9).
Liao X
et al.
Genetic associations between voltage-gated calcium channels and autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review.
Mol Brain, 2020Jun22, 13 (96).
Nieto-Rostro M
et al.
Ablation of α2δ-1 inhibits cell-surface trafficking of endogenous N-type calcium channels in the pain pathway in vivo.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018Dec18, 115 (E12043-E12052).
D'Arco M
et al.
The upregulation of α2δ-1 subunit modulates activity-dependent Ca2+ signals in sensory neurons.
J. Neurosci.,
2015
Apr
15
, 35 (5891-903).
Patel R
et al.
α2δ-1 gene deletion affects somatosensory neuron function and delays mechanical hypersensitivity in response to peripheral nerve damage.
J. Neurosci.,
2013
Oct
16
, 33 (16412-26).
Satake S
et al.
Cav2.1 channels control multivesicular release by relying on their distance from exocytotic Ca2+ sensors at rat cerebellar granule cells.
J. Neurosci.,
2014
Jan
22
, 34 (1462-74).
Contributors: Rajnish Ranjan, Michael Schartner
To cite this page: [Contributors] Channelpedia https://channelpedia.epfl.ch/wikipages/79/ , accessed on 2026 Feb 18