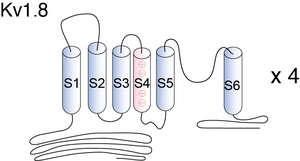
Kv1.8
Gene: Kcna10 Alias: Kv1.8, kcna10
Kv1.8, encoded by the gene KCNA10, is a member of the potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A. Kv1.8 plays a central role in cardiac atria repolarization [386]. KCNA10 is primarily expressed by hair cells of the inner ear [1654]. It is specifically regulated by cGMP and postulated to mediate the effects of substances that increase intracellular cGMP.
Experimental data
Rat Kv1.8 gene in CHO host cells |
||
|
Click for details 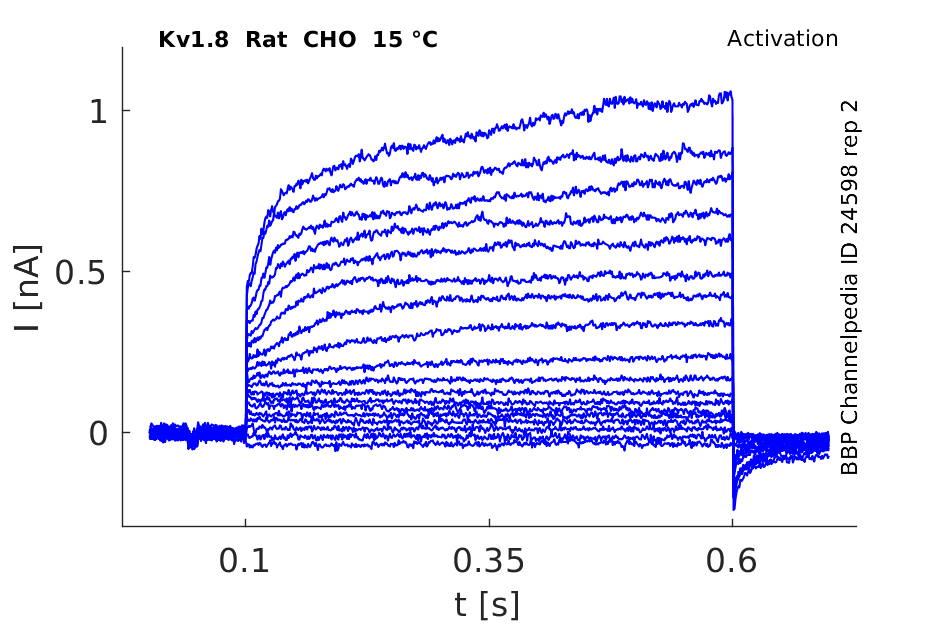
15 °Cshow 145 cells |
Click for details 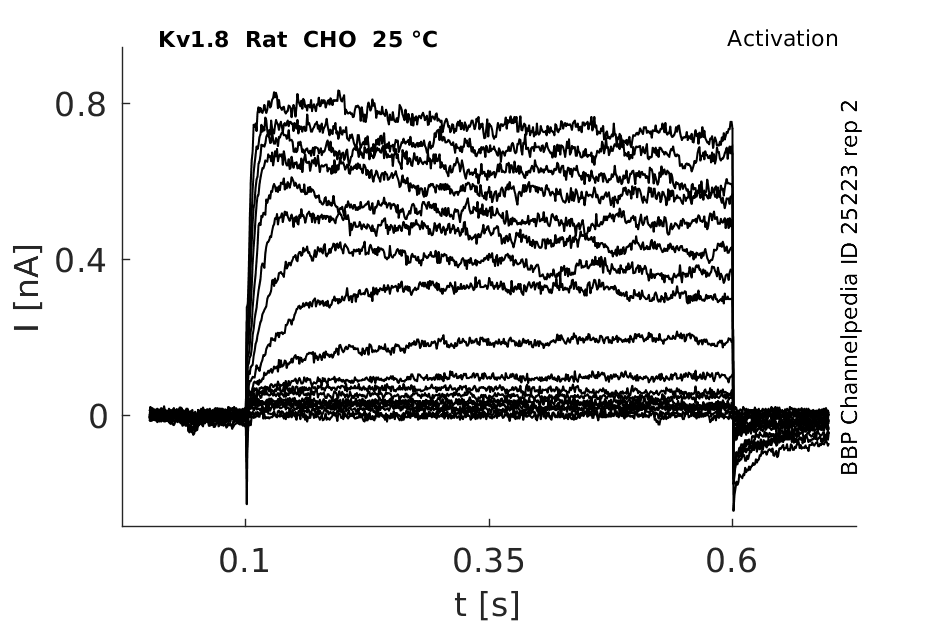
25 °Cshow 217 cells |
Click for details 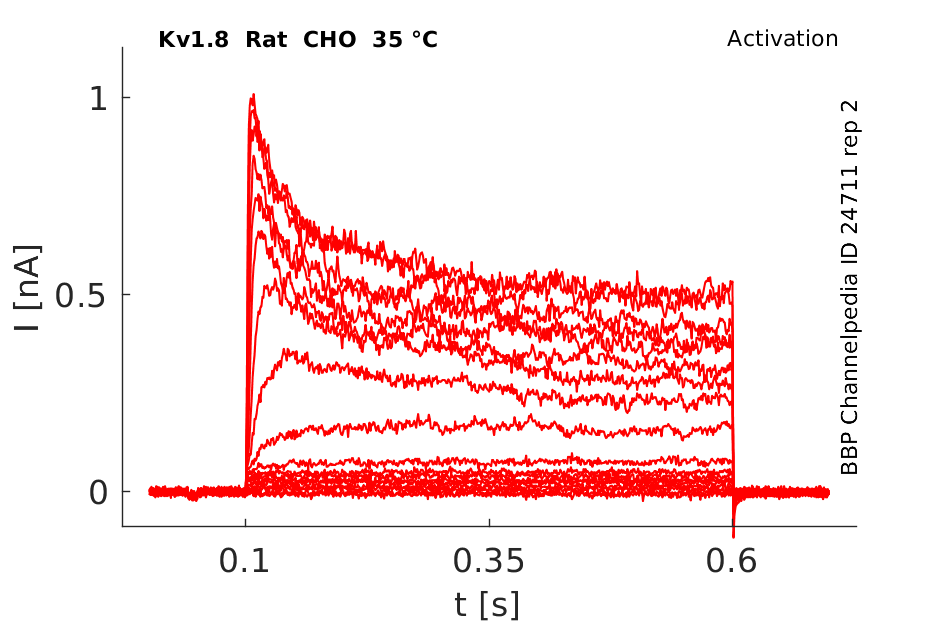
35 °Cshow 190 cells |
Human KCNA10 is intronless, and is clustered with genes KCNA2 and KCNA3 on chromosome 1 at p13.1 r p22.1. Finer mapping of the gene was achieved by PCR of a set of CEPH YAC clones that spanned the region of interest. Human KCNA10 resides within the genetic interval defined by microsatellite loci D1S2809 and D1S2726.[611]
Transcript
| Species | NCBI accession | Length (nt) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | NM_005549.2 | 1959 | |
| Mouse | NM_001081140.1 | 1826 | |
| Rat | NM_001191713.1 | 1755 |
KCNA10 shares 50–70% amino acid sequence identity with other KCNA protein family members [1654]
Isoforms
Post-Translational Modifications
Visual Representation of Kv1.8 Structure
Methodology for visual representation of structure available here
Structure of Kv1.8
KV1.8 contains six membrane-spanning domains with a shaker-type repeat in the fourth segment and a pore (P) region. Its most distinguishing feature is the presence of a putative cyclic nucleotide-binding (CNB) domain at the COOH terminus. It is specifically regulated by cGMP and postulated to mediate the effects of substances that increase intracellular cGMP1. The channel displays an unusual inhibitor profile, because in addition to being blocked by classical K+ channel blockers, it is also sensitive to inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide gated cation channel such as verapamil and pimozide [610]
KCNA10 is 90% identical to Kcn1 at the amino acid level, and its secondary structure is the same, including a putative cGMP-binding domain at the COOH terminus. [612]
Although KCNA10 is suspected to have a similar secondary structure to all KCNA channels it is unique among the KCNA family due to its putative cyclic nucleotide-binding domain at the carboxyl terminus [1654]
Kv1.8 predicted AlphaFold size
Methodology for AlphaFold size prediction and disclaimer are available here
Kv1.8

Single Channel Kinetics

Hodgkin and Huxley Model of Kv1.8

Expression in Tissue
KCNA10 is a cyclic nucleotide-gated, voltage-activated K channel that is detected in kidney, heart, and aorta by Northern blot. [608]
KCNA10 Not expressed in Brain
Multiple organs from the adult Kcna10TM45 were examined for beta-galactosidase (Kcna10 promoter and enhancers) expression. Brain, heart, lung, and liver from heterozygous and homozygous Kcna10TM45 mice did not exhibit any beta-galactosidase expression. Kidney expression could not be evaluated due to endogenous beta-galactosidase-like activity in the wild type kidney [1654]
KCNA4B's message expression parallels, to a large extent, that of KCNA10, with predominant expression in heart, kidney, and skeletal muscle, but not in brain [610]
Hair cells of the inner ear
In hair cells of the Corti organ KCNA10 shows strong expression.[1655]
KCNA10 is primarily expressed in hair cells in the vestibular organs and the organ of Corti in the inner ear as was also shown by a study using reporter genes. KCNA10 expression follows a gradient opposite to the tonotopic gradient. However, KCNA10 null mice displayed mild hearing deficits and significant but not overt vestibular dysfunction. [1654]
KCNA10 protein was easily detectable at the apical membrane of rat proximal tubular cells, and a weaker signal was also evident in the glomerulus. In situ hybridization experiments confirmed the immunocytochemical studies and revealed KCNA10 expression in human proximal tubular cells, glomerular and vascular endothelial cells, and also in vascular smooth muscle cells. The data suggest that KCNA10 may facilitate proximal tubular sodium absorption by stabilizing cell membrane voltage [608]
KCNA10 protein was easily detectable at the apical membrane of rat proximal tubular cells, and a weaker signal was also evident in the glomerulus.[608].
Several types of voltage-gated K+ (Kv) channel, such as KCNQ1, KCNA10 and Kv1.3, are highly expressed at the apical membrane of proximal tubules and distal tubules. They may participate in stabilizing the cell membrane potential [1660]
Root cells
Vascularization
Kv1.8 participates in renal K metabolism and regulates vascular tone. [608]
Auditory function
A recent study showed that a null mutation of mouse KCNA10 causes significant vestibular and mild hearing dysfunction [1654]
QT Syndrome
In addition KCNA10 has been associated with Long QT syndrome (LQTS), an arrhythmogenic disorder characterized by prolongation of the QT interval on electrocardiograms (ECGs) [611]
Disorientation
The KCNA10-null mouse does not exhibit any obvious imbalance behaviors such as circling, weaving, or head-bobbing, and swimming behavior that relies on the gravity sensing organs was normal [1654]
barium tetraethylammonium and 4-aminopyridine
KCNA10 currents are being blocked by classical K channel blockers (barium tetraethylammonium and 4-aminopyridine). It is also sensitive to inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) cation channels (verapamil and pimozide). The phorbol ester phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, an activator of protein kinase C, inhibited whole cell current by 42%. [612]
1.3
Interestingly, Kv1.3 and KCNA10 are located on chromosome 1 at p13.1 and are probably the result of gene duplication. Taken together, these data strongly suggest that KCNA10 has pharmacological properties common to both voltage-gated K channels and CNG cation channels [612]
kv1.4
Kcna10 is regulated in part by the soluble β subunit Kcna4b, which increases overall Kcna10 current and is currently thought to mediate upregulation of Kcna10 activity by cAMP and downregulation by cGMP [1655]
Verapimil

KCNA4B
When injected alone in oocytes, KCNA4B produced no detectable current. However, when coinjected with KCNA10, it increased KCNA10 current expression by nearly threefold. In addition, the current became more sensitive to activation by cAMP. KCNA4B can be coimmunoprecipitated with the COOH terminus of KCNA10 and full-length KCNA10. It encodes a soluble protein (141 aa) with no amino acid homology to known beta-subunits but with limited structural similarity to the NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductase superfamily [610]
References
Bailey SD
et al.
Variation at the NFATC2 locus increases the risk of thiazolidinedione-induced edema in the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) study.
Diabetes Care,
2010
Oct
, 33 (2250-3).
Talmud PJ
et al.
Gene-centric association signals for lipids and apolipoproteins identified via the HumanCVD BeadChip.
Am. J. Hum. Genet.,
2009
Nov
, 85 (628-42).
Gutman GA
et al.
International Union of Pharmacology. LIII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of voltage-gated potassium channels.
Pharmacol. Rev.,
2005
Dec
, 57 (473-508).
Strausberg RL
et al.
Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,
2002
Dec
24
, 99 (16899-903).
Yao X
et al.
Expression of KCNA10, a voltage-gated K channel, in glomerular endothelium and at the apical membrane of the renal proximal tubule.
J. Am. Soc. Nephrol.,
2002
Dec
, 13 (2831-9).
Landes GM
et al.
Molecular characterization and refined genomic localization of three human potassium ion channel genes.
Cytogenet. Cell Genet.,
1995
, 70 (280-4).
Tian S
et al.
Regulation of the voltage-gated K+ channel KCNA10 by KCNA4B, a novel beta-subunit.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol.,
2002
Jul
, 283 (F142-9).
Orias M
et al.
Genomic localization of the human gene for KCNA10, a cGMP-activated K channel.
Genomics,
1997
May
15
, 42 (33-7).
Lang R
et al.
KCNA10: a novel ion channel functionally related to both voltage-gated potassium and CNG cation channels.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol.,
2000
Jun
, 278 (F1013-21).
Archer SL
et al.
Nitric oxide and cGMP cause vasorelaxation by activation of a charybdotoxin-sensitive K channel by cGMP-dependent protein kinase.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,
1994
Aug
2
, 91 (7583-7).
Lee SI
et al.
A null mutation of mouse Kcna10 causes significant vestibular and mild hearing dysfunction.
Hear. Res.,
2013
Jun
, 300 (1-9).
Carlisle FA
et al.
Specific expression of Kcna10, Pxn and Odf2 in the organ of Corti.
Gene Expr. Patterns,
2012 May-Jun
, 12 (172-9).
Wang W
Renal potassium channels: recent developments.
Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens.,
2004
Sep
, 13 (549-55).
Jagger DJ
et al.
The Membrane Properties of Cochlear Root Cells are Consistent with Roles in Potassium Recirculation and Spatial Buffering.
J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol.,
2010
Apr
15
, ().
Tsantoulas C
et al.
Kv2 dysfunction after peripheral axotomy enhances sensory neuron responsiveness to sustained input.
Exp. Neurol.,
2014
Jan
, 251 (115-26).
Contributors: Rajnish Ranjan, Michael Schartner, Nitin Khanna, Katherine Johnston
To cite this page: [Contributors] Channelpedia https://channelpedia.epfl.ch/wikipages/8/ , accessed on 2026 Feb 23