Kir3.4
Description: potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 5 Gene: Kcnj5 Alias: Kir3.4, Girk4, kcnj5
KCNJ5 (also known as CIR; GIRK4; KATP1; LQT13; KIR3.4) encodes Kir3.4, a potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 5. This integral membrane protein has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell and is controlled by G-proteins. It may associate with two other G-protein-activated potassium channels to form a heteromultimeric pore-forming complex. In contrast to the other mammalian GIRK family members, GIRK1 can not form functional channels by itself and has to assemble with GIRK2, 3 or 4 (Mark[199]).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/3762
Experimental data
Rat Kir3.4 gene in CHO host cells |
||
|
Click for details 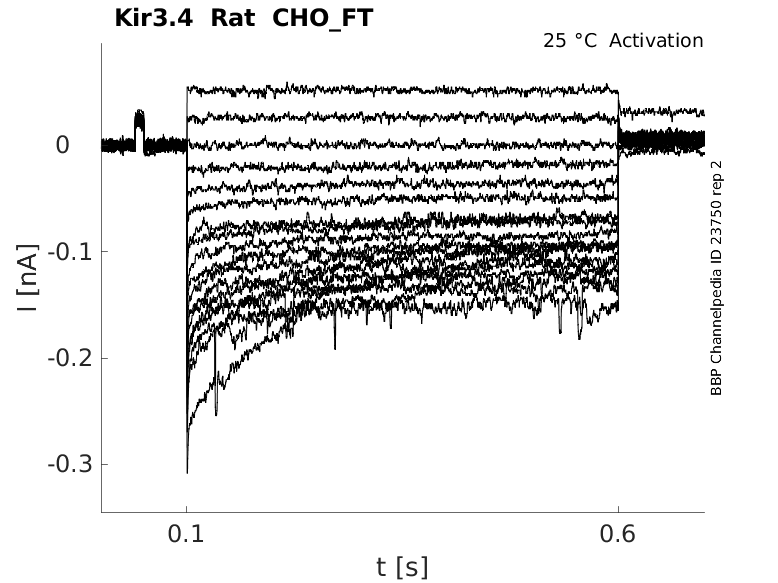
25 °Cshow 44 cells |
Click for details 
35 °Cshow 14 cells |
|
Gene
Transcript
| Species | NCBI accession | Length (nt) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | NM_000890.5 | 6068 | |
| Mouse | NM_010605.5 | 4679 | |
| Rat | NM_017297.2 | 3335 |
Protein Isoforms
Isoforms
Post-Translational Modifications
Structure
Kir3.4 predicted AlphaFold size
Methodology for AlphaFold size prediction and disclaimer are available here
Kir3.1 is expressed in the heart and brain (Kubo [1000]), and is known to assemble with Kir3.4 in SAN and atrial myocytes in the heart and with Kir3.2 in the brain to form functional channels (Krapivinsky [998], Velimirovic [999]).
Kir3.1 and Kir3.4, expressed mainly in SAN and atrial myocytes in the heart, form heterotetrameric channels, which are coupled to m2 muscarinic receptor via G-protein bc subunits and carry the ACh-activated K+ current (IK,ACh) regulating the heart rate (Krapivinsky [998], Corey [1001]).
Mice deficient of Kir3.1 or 3.4 exhibit mild resting tachycardia (Bettahi [1005]) and impaired beat-to-beat control (Wickman [1006]).
Kir3.4 deficient mice were resistant to atrial fibrillation caused by vagal stimulation (Kovoor [1007]). Kir3.4 could be predisposing to or even protecting against atrial fibrillation (Calloe [997]).
Co-expression of Kir2.1 with Kir3.4 in Xenopus oocytes and HEK293T cells did not yield currents with distinguishable features. However, co-expression of a dominant-negative Kir2.1 with the wild-type Kir3.4 decreased the Kir3.4 current amplitude in Xenopus oocytes. The results indicate that Kir2.1 is capable of forming heteromultimeric channels with Kir3.4. (Ishihara [996])
Stimulation of the M2 receptor by ACh causes dissociation of the coupled G-protein and the Gbc-subunits activate the Kir3.1/3.4 channel by direct binding (Logothetis [1002]).
phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2) is a requirement for Kir channels activity and a decrease in bound PIP2 strongly decreases the open probability of the Kir3.1/ 3.4 channels (Huang [1003], Sui [1004]).
GIRK1/4 channel current can be blocked by BaCl(2) and enhanced by increasing the driving force for K(+) across the cell membrane. (Walsh [995])
References
Jelacic TM
et al.
Functional expression and characterization of G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channels containing GIRK3.
J. Membr. Biol.,
1999
May
15
, 169 (123-9).
Saitoh O
et al.
RGS7 and RGS8 differentially accelerate G protein-mediated modulation of K+ currents.
J. Biol. Chem.,
1999
Apr
2
, 274 (9899-904).
A C-terminal peptide of the GIRK1 subunit directly blocks the G protein-activated K+ channel (GIRK) expressed in Xenopus oocytes.
J. Physiol. (Lond.), 1997 Nov 15 , 505 ( Pt 1) (13-22).
Mark MD
et al.
G-protein mediated gating of inward-rectifier K+ channels.
Eur. J. Biochem.,
2000
Oct
, 267 (5830-6).
Slesinger PA
Ion selectivity filter regulates local anesthetic inhibition of G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channels.
Biophys. J.,
2001
Feb
, 80 (707-18).
Kracke GR
et al.
The cannabinoid receptor agonists, anandamide and WIN 55,212-2, do not directly affect mu opioid receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol.,
2007
Dec
, 376 (285-93).
Walsh KB
A real-time screening assay for GIRK1/4 channel blockers.
J Biomol Screen,
2010
Dec
, 15 (1229-37).
Ishihara K
et al.
Heteromeric assembly of inward rectifier channel subunit Kir2.1 with Kir3.1 and with Kir3.4.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,
2009
Mar
20
, 380 (832-7).
Calloe K
et al.
Characterizations of a loss-of-function mutation in the Kir3.4 channel subunit.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,
2007
Dec
28
, 364 (889-95).
Krapivinsky G
et al.
The G-protein-gated atrial K+ channel IKACh is a heteromultimer of two inwardly rectifying K(+)-channel proteins.
Nature,
1995
Mar
9
, 374 (135-41).
Velimirovic BM
et al.
The K+ channel inward rectifier subunits form a channel similar to neuronal G protein-gated K+ channel.
FEBS Lett.,
1996
Jan
22
, 379 (31-7).
Kubo Y
et al.
Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel.
Nature,
1993
Aug
26
, 364 (802-6).
Corey S
et al.
Number and stoichiometry of subunits in the native atrial G-protein-gated K+ channel, IKACh.
J. Biol. Chem.,
1998
Feb
27
, 273 (5271-8).
Logothetis DE
et al.
The beta gamma subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart.
Nature,
1987 Jan 22-28
, 325 (321-6).
Huang CL
et al.
Direct activation of inward rectifier potassium channels by PIP2 and its stabilization by Gbetagamma.
Nature,
1998
Feb
19
, 391 (803-6).
Sui JL
et al.
Na+ activation of the muscarinic K+ channel by a G-protein-independent mechanism.
J. Gen. Physiol.,
1996
Nov
, 108 (381-91).
Bettahi I
et al.
Contribution of the Kir3.1 subunit to the muscarinic-gated atrial potassium channel IKACh.
J. Biol. Chem.,
2002
Dec
13
, 277 (48282-8).
Wickman K
et al.
Abnormal heart rate regulation in GIRK4 knockout mice.
Neuron,
1998
Jan
, 20 (103-14).
Kovoor P
et al.
Evaluation of the role of I(KACh) in atrial fibrillation using a mouse knockout model.
J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.,
2001
Jun
15
, 37 (2136-43).
Credits
To cite this page: [Contributors] Channelpedia https://channelpedia.epfl.ch/wikipages/49/ , accessed on 2026 Feb 24