Kv6.2
Description: potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 2 Gene: Kcng2 Alias: Kv6.2, kcng2
Kv6.2, encoded by the gene KCNG2, is a member is a gamma subunit of the voltage-gated potassium channel, subfamily G. Kv6.2 is thought to be a delayed-rectifier type channels that may contribute to cardiac action potential repolarization. NCBI
Experimental data
Rat Kv6.2 gene in CHO host cells |
||
|
Click for details 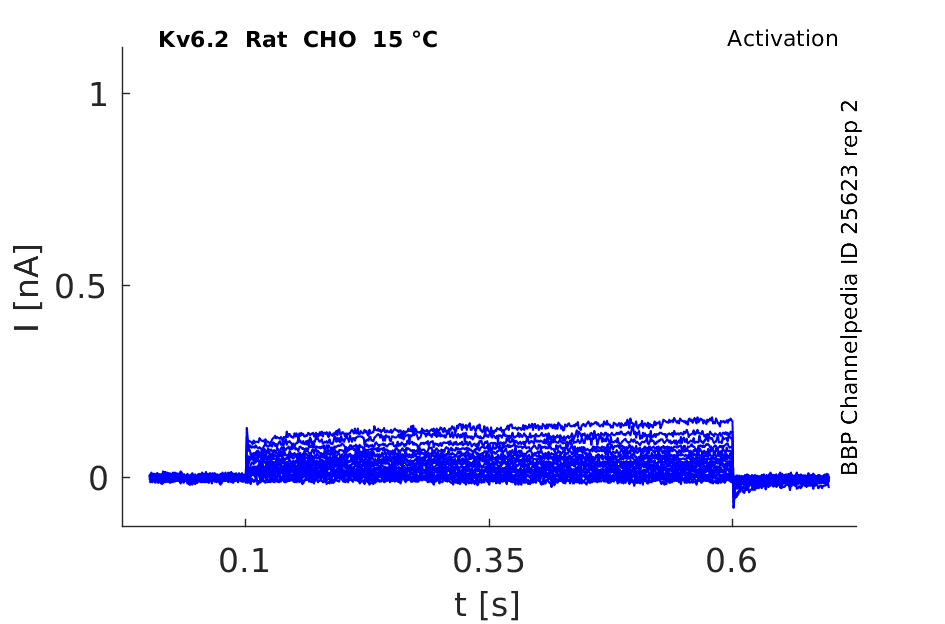
15 °Cshow 61 cells |
Click for details 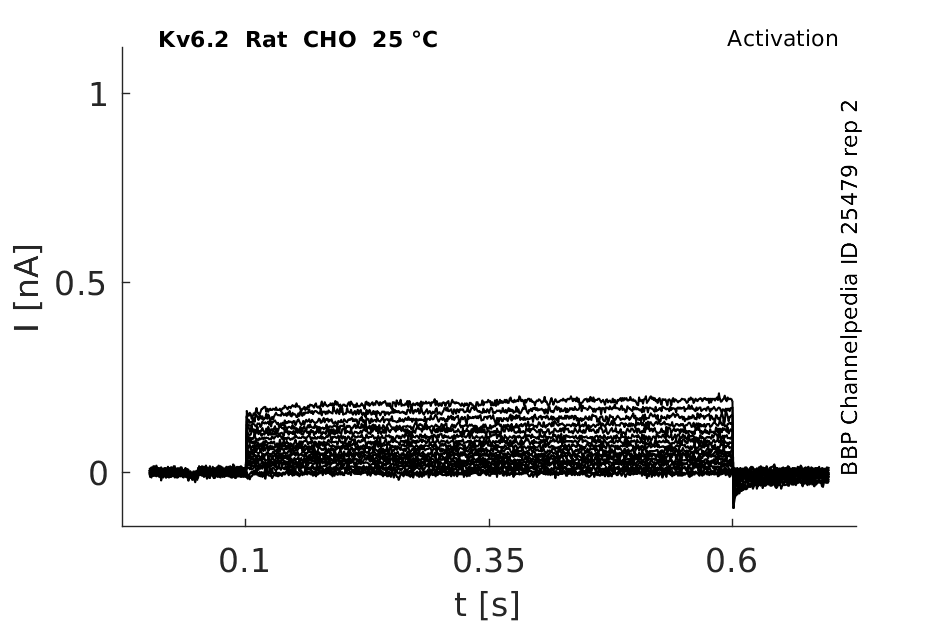
25 °Cshow 57 cells |
Click for details 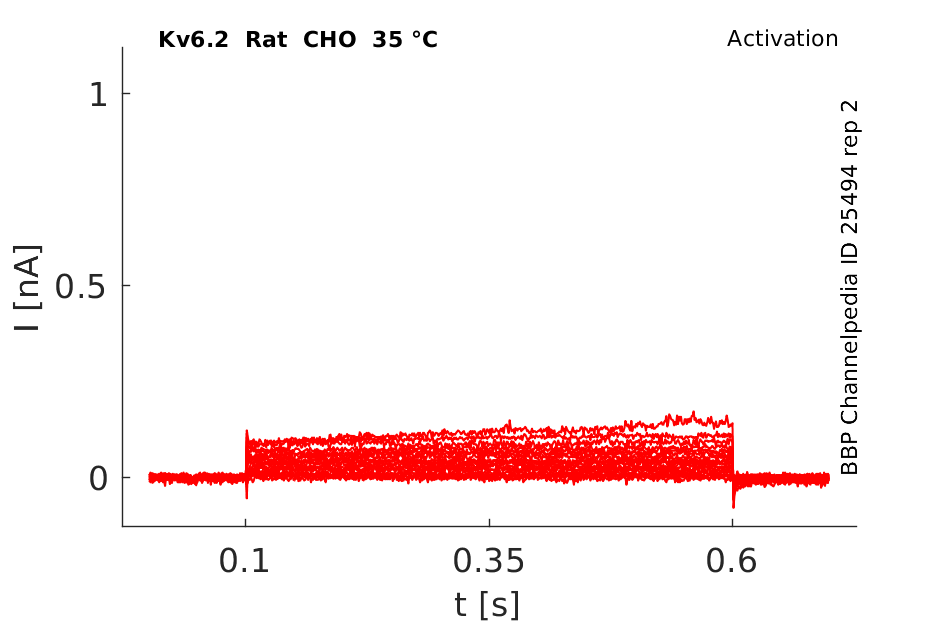
35 °Cshow 84 cells |
Gene
Transcript
| Species | NCBI accession | Length (nt) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | NM_012283.2 | 1876 | |
| Mouse | NM_001190373.1 | 2815 | |
| Rat | NM_001107372.1 | 1838 |
Protein Isoforms
Isoforms
Post-Translational Modifications
Visual Representation of Kv6.2 Structure
Methodology for visual representation of structure available here
Yeast two-hybrid reporter assays indicated that Kv6.2 amino-termini are able to interact specifically with the Kv2.1 amino-terminus. It is proposed that this protein protein interaction underlies Kv2.1/Kv6.2 subunit assembly and the expression of functional heteromultimeric Kv2.1/Kv6.2 channels. [661]
Kv6.2 predicted AlphaFold size
Methodology for AlphaFold size prediction and disclaimer are available here
Kv6.2
Rat and human Kv6.2 subunits appear to be unable to form functional Kv channels in a heterologous expression system, but, when coexpressed with Kv2.1 alpha subunits, heteromultimeric Kv channels were formed mediating voltage-activated delayed-rectifier type outward currents. Their kinetics and conductance-voltage relationship were different from those mediated by homomultimeric Kv2.1 channels [661]
Effects of heteromerization with Kv6 subunits on the time course of inactivation of Kv2. 1 channels

Kv6.2 Expressed in Heart
Kv6.2 mRNA is preferentially expressed in rat and human myocard. [661]
Kv6.2 Expressed in Rat Brain
According to the Mus musculus potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily G, member 2 (Kcng2) mRNA expression as been seen in the visual cortex NCBI
Rat and human Kv6.2 subunits appear to be unable to form functional Kv channels in a heterologous expression system, but, when coexpressed with Kv2.1 alpha subunits, heteromultimeric Kv channels were formed mediating voltage-activated delayed-rectifier type outward currents. [661]
Delayed-rectifier type channels containing Kv6.2 subunits may contribute to cardiac action potential repolarization. [661]
Kv2.1/Kv6.2 channels display submicromolar sensitivity to the antiarrhythmic drug propafenone. [661]
References
Rettig J
et al.
Inactivation properties of voltage-gated K+ channels altered by presence of beta-subunit.
Nature,
1994
May
26
, 369 (289-94).
Kramer JW
et al.
Modulation of potassium channel gating by coexpression of Kv2.1 with regulatory Kv5.1 or Kv6.1 alpha-subunits.
Am. J. Physiol.,
1998
Jun
, 274 (C1501-10).
Isacoff EY
et al.
Evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric potassium channels in Xenopus oocytes.
Nature,
1990
Jun
7
, 345 (530-4).
Jegla T
et al.
A novel subunit for shal K+ channels radically alters activation and inactivation.
J. Neurosci.,
1997
Jan
1
, 17 (32-44).
Namba N
et al.
Kir2.2v: a possible negative regulator of the inwardly rectifying K+ channel Kir2.2.
FEBS Lett.,
1996
May
20
, 386 (211-4).
Chen TY
et al.
A new subunit of the cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel in retinal rods.
Nature,
1993
Apr
22
, 362 (764-7).
Liman ER
et al.
A second subunit of the olfactory cyclic nucleotide-gated channel confers high sensitivity to cAMP.
Neuron,
1994
Sep
, 13 (611-21).
Bradley J
et al.
Heteromeric olfactory cyclic nucleotide-gated channels: a subunit that confers increased sensitivity to cAMP.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,
1994
Sep
13
, 91 (8890-4).
Biel M
et al.
Molecular cloning and expression of the Modulatory subunit of the cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel.
J. Biol. Chem.,
1996
Mar
15
, 271 (6349-55).
Zhu XR
et al.
Structural and functional characterization of Kv6.2 a new gamma-subunit of voltage-gated potassium channel.
Recept. Channels,
1999
, 6 (337-50).
Ottschytsch N
et al.
Domain analysis of Kv6.3, an electrically silent channel.
J. Physiol. (Lond.),
2005
Nov
1
, 568 (737-47).
Contributors: Rajnish Ranjan, Michael Schartner, Katherine Johnston
To cite this page: [Contributors] Channelpedia https://channelpedia.epfl.ch/wikipages/20/ , accessed on 2026 Feb 25