Kv11.3
Description: potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 7 Gene: Kcnh7 Alias: Kv11.3, erg3, kcnh7, HERG3
Kv11.3, encoded by the gene KCNH7 , is a voltage-activated potassium channel belonging to the eag family.
Experimental data
Rat Kv11.3 gene in CHO host cells datasheet |
||
|
Click for details 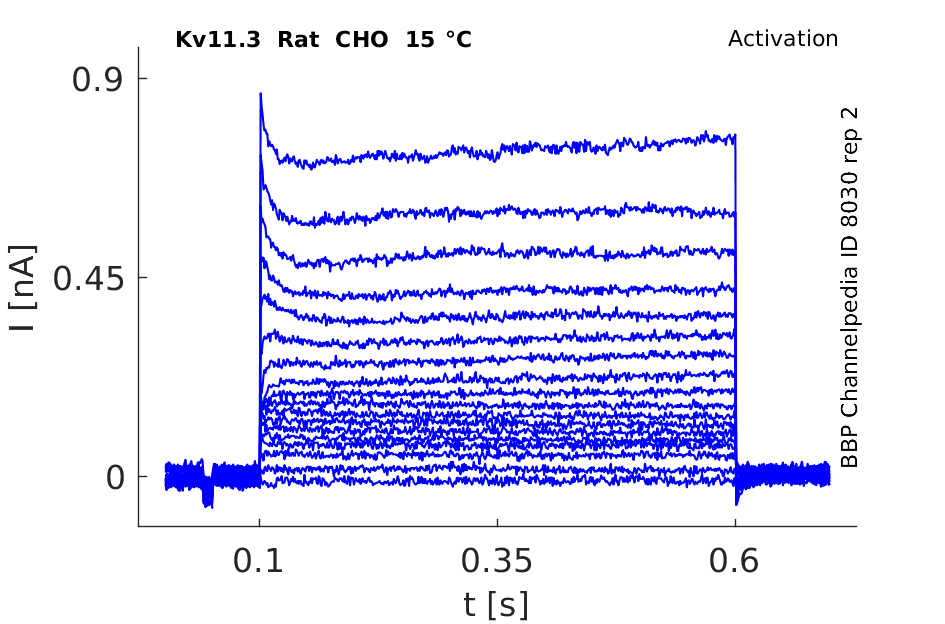
15 °Cshow 100 cells |
Click for details 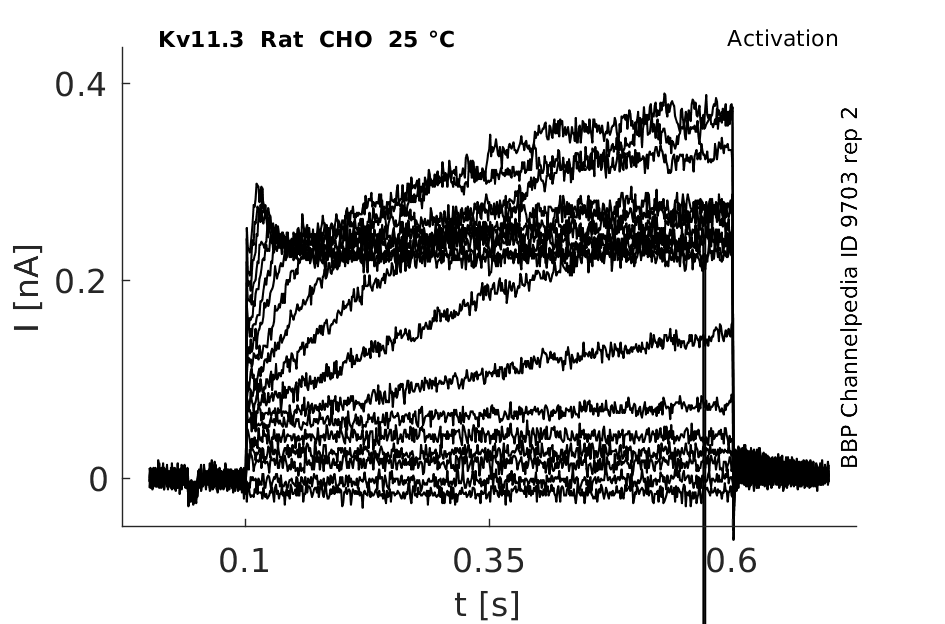
25 °Cshow 96 cells |
Click for details 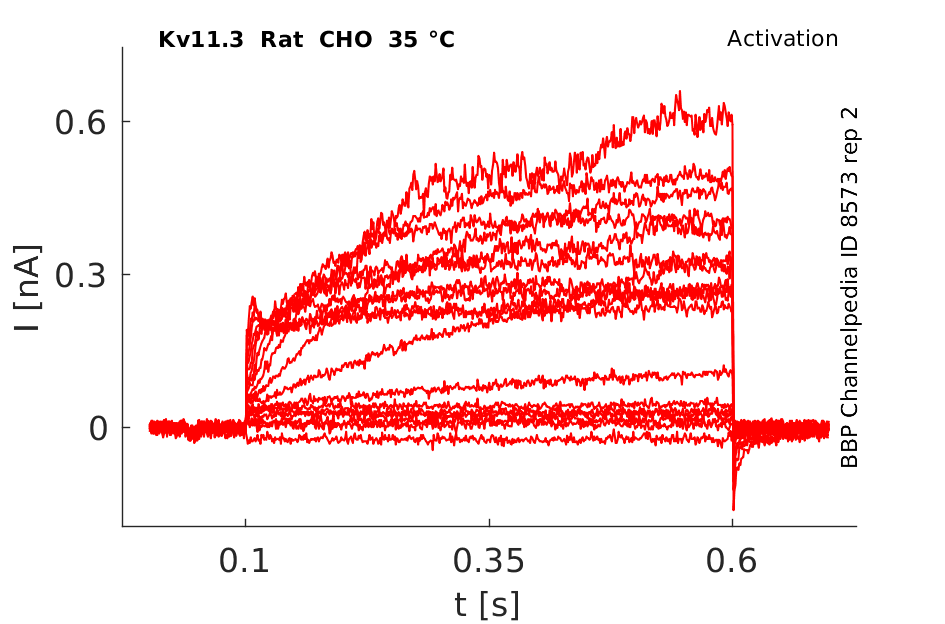
35 °Cshow 104 cells |
Gene
Transcript
| Species | NCBI accession | Length (nt) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | NM_033272.4 | 4262 | |
| Mouse | NM_133207.2 | 3798 | |
| Rat | NM_131912.1 | 3807 |
Protein Isoforms
Isoforms
Post-Translational Modifications
Visual Representation of Kv11.3 Structure
Methodology for visual representation of structure available here
The ether-a-go-go gene K+ channel alpha-subunits consist of six membrane-spanning domains (S1–S6). A Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) domain is located at the N-terminus and a cyclic nucleotide-binding domain (cNBD) in the C-terminus. This, and the tetrameric structure of a K+ channel can be seen in fig1 of Bauer [778]. The pore region P and S6 may form the inner core of the channel, S1–S5 the outer parts of the channel with S4 as the voltage sensor. [778]
Kv11.3 predicted AlphaFold size
Methodology for AlphaFold size prediction and disclaimer are available here
Human Kv11.3 inactivation in X oocytes

As expected, hKv11.3 inactivation was considerably slower than hKv11.1 and hKv11.2, which display similar inactivation rate [796].
Rat Herg3 (rKv11.3) expressed in CHO cells

Herg3 Expression in the Brain in Rats
HERG2 and HERG3 are expressed exclusively in brain [1743] All three Kv11 channels are expressed in the olfactory bulb, and erg1 and erg3 are co-expressed in the reticular thalamic nucleus, cerebral cortex, cerebellum and hippocampus [327]. Single cell RT-PCR experiments have shown that the erg subunits can be expressed in different combinations in individual rat lactotroph cells [781]. In addition, transcripts for more than one erg subunit have been detected in various cell lines: NG108-15 (neuroblastoma, erg1–3, [793]), PC12 (sympathetic ganglia neuron, erg1 and erg2, [327]), MMQ (lactotroph, erg1–3, [794]) and GH3/B6 (somatomammotroph, erg1 and erg2, [789]).
Kv11.2 and Kv11.3 are thought, contrary to Kv11.1, to be found exclusively in the nervous system [790]. However Kv11.2 and Kv11.3 transcripts were shown in rat pancreatic islets [798]. In rodent brain, the three channel subtypes display a widespread expression pattern [799], [326], [327]. although one study [327] did detect Kv11.2 almost exclusively in the olfactory bulb. (From [796])
The erg3 gene is broadly expressed throughout the nervous system, similar to erg1. In addition to brain,erg3 mRNA is expressed in all of the sympathetic ganglia tested and also is expressed at low levels in retina [790]
Association of Kv11.3 with bipolar spectrum disorders
Several mutations of Kv11.3 potassium channels were associated with the pathophysiology of bipolar spectrum disorders, particularly with bipolar 1 disorder, in genome-wide association studies. [2089] [2090]
BeKm-1 and APETx1
The toxins BeKm-1 and APETx1 reduced the currents mediated by erg1a and erg1a/erg3 concatemers to a similar degree as the erg current of Purkinje cells. A–D, BeKm-1 (100 nM) or APETx1 (1 μM) were applied to HEK 293 cells stably expressing erg1a, erg2, erg3, or concatemeric erg1a/erg3 channels.
References
Wimmers S
et al.
Biophysical properties of heteromultimeric erg K+ channels.
Pflugers Arch.,
2002
Dec
, 445 (423-30).
Papa M
et al.
Expression pattern of the ether-a-gogo-related (ERG) K+ channel-encoding genes ERG1, ERG2, and ERG3 in the adult rat central nervous system.
J. Comp. Neurol.,
2003
Nov
3
, 466 (119-35).
Saganich MJ
et al.
Differential expression of genes encoding subthreshold-operating voltage-gated K+ channels in brain.
J. Neurosci.,
2001
Jul
1
, 21 (4609-24).
Akbarali HI
et al.
Role of HERG-like K(+) currents in opossum esophageal circular smooth muscle.
Am. J. Physiol.,
1999
Dec
, 277 (C1284-90).
Bauer CK
et al.
A functional role of the erg-like inward-rectifying K+ current in prolactin secretion from rat lactotrophs.
Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.,
1999
Feb
25
, 148 (37-45).
Sanguinetti MC
et al.
A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel.
Cell,
1995
Apr
21
, 81 (299-307).
Overholt JL
et al.
HERG-Like potassium current regulates the resting membrane potential in glomus cells of the rabbit carotid body.
J. Neurophysiol.,
2000
Mar
, 83 (1150-7).
Bauer CK
et al.
RERG is a molecular correlate of the inward-rectifying K current in clonal rat pituitary cells.
Recept. Channels,
1998
, 6 (19-29).
Shi W
et al.
Identification of two nervous system-specific members of the erg potassium channel gene family.
J. Neurosci.,
1997
Dec
15
, 17 (9423-32).
Wimmers S
et al.
Erg1, erg2 and erg3 K channel subunits are able to form heteromultimers.
Pflugers Arch.,
2001
Jan
, 441 (450-5).
Meves H
et al.
Separation of M-like current and ERG current in NG108-15 cells.
Br. J. Pharmacol.,
1999
Jul
, 127 (1213-23).
Lecchi M
et al.
Isolation of a long-lasting eag-related gene-type K+ current in MMQ lactotrophs and its accommodating role during slow firing and prolactin release.
J. Neurosci.,
2002
May
1
, 22 (3414-25).
Einarsen K
et al.
Functional properties of human neuronal Kv11 channels.
Pflugers Arch.,
2009
Aug
, 458 (689-700).
Chiesa N
et al.
A novel role for HERG K+ channels: spike-frequency adaptation.
J. Physiol. (Lond.),
1997
Jun
1
, 501 ( Pt 2) (313-8).
Mühlbauer E
et al.
Circadian changes of ether-a-go-go-related-gene (Erg) potassium channel transcripts in the rat pancreas and beta-cell.
Cell. Mol. Life Sci.,
2007
Mar
, 64 (768-80).
Guasti L
et al.
Expression pattern of the ether-a-go-go-related (ERG) family proteins in the adult mouse central nervous system: evidence for coassembly of different subunits.
J. Comp. Neurol.,
2005
Oct
17
, 491 (157-74).
Cordeiro S
et al.
Expression pattern of Kv11 (Ether à-go-go-related gene; erg) K+ channels in the mouse retina.
PLoS ONE,
2011
, 6 (e29490).
Niculescu D
et al.
Erg potassium currents of neonatal mouse Purkinje cells exhibit fast gating kinetics and are inhibited by mGluR1 activation.
J. Neurosci.,
2013
Oct
16
, 33 (16729-40).
Polvani S
et al.
Developmentally regulated expression of the mouse homologues of the potassium channel encoding genes m-erg1, m-erg2 and m-erg3.
Gene Expr. Patterns,
2003
Dec
, 3 (767-76).
Bilet A
et al.
Effects of the small molecule HERG activator NS1643 on Kv11.3 channels.
PLoS ONE,
2012
, 7 (e50886).
Strauss KA
et al.
A population-based study of KCNH7 p.Arg394His and bipolar spectrum disorder.
Hum. Mol. Genet.,
2014
Dec
1
, 23 (6395-406).
Kuo PH
et al.
Identification of novel loci for bipolar I disorder in a multi-stage genome-wide association study.
Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry,
2014
Jun
3
, 51 (58-64).
Contributors: Katherine Johnston
To cite this page: [Contributors] Channelpedia https://channelpedia.epfl.ch/wikipages/37/ , accessed on 2026 Feb 25
