Kir6.1
Description: potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 8 Gene: Kcnj8 Alias: Kir6.1, kcnj8, sltr, gnite, slmbr
KATP channels are present in most, if not all, excitable tissues, and share the property of being inhibited by intracellular nucleotide triphosphates (Ashcroft 1988 [1048]). Structurally unique amongst K channels, these KATP channels are formed by coexpression of an ABC protein (SUR1, or SUR2; Aguilar-Bryan et al., 1995 [1049]; Inagaki et al., 1996 [1050]) and an inward rectifier K channel subunit (Kir6.1 or Kir6.2; Inagaki et al., 1995a [1051], b [1052]; Inagaki et al., 1996 [1050]). Expression of Kir6.2 alone does not result in functional ion channels, suggesting an intimate and requisite interaction between these two subunits. (Shyng [207])
The gene KCNJ8 (also known as KIR6.1; uKATP-1) encodes Kir6.1, an integral membrane protein, inward-rectifier type potassium channel, subfamily J, member 8. The encoded protein, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, is controlled by G-proteins.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/3764
Experimental data
Rat Kir6.1 gene in CHO host cells |
||
|
Click for details 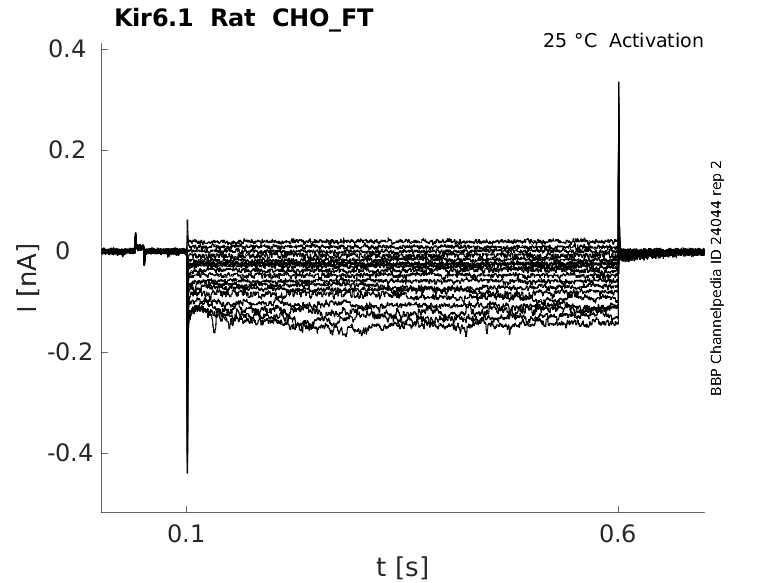
25 °Cshow 39 cells |
Click for details 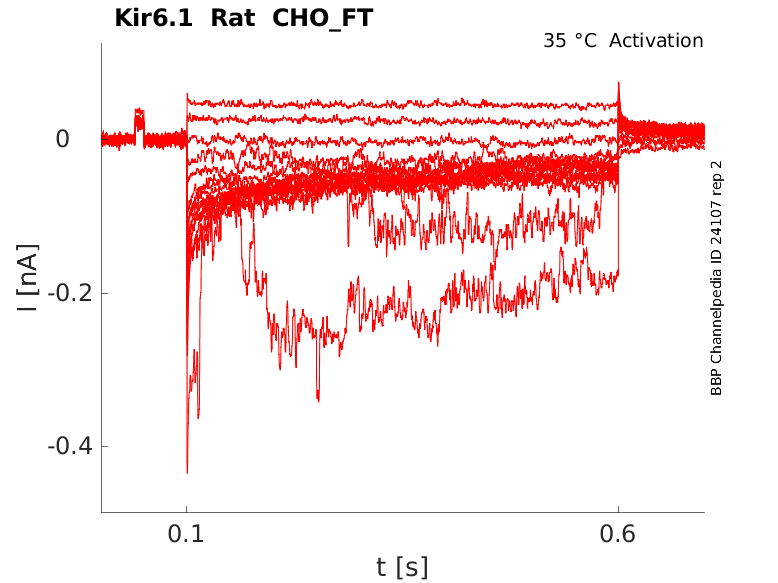
35 °Cshow 11 cells |
|
Gene
Transcript
| Species | NCBI accession | Length (nt) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | NM_004982.4 | 2274 | |
| Mouse | NM_008428.5 | 2564 | |
| Rat | NM_017099.4 | 1577 |
Protein Isoforms
Isoforms
Post-Translational Modifications
The KATP channel is an octameric complex comprised of four Kir6.0 subunits from the inward rectifier family of potassium channels and four sulfonylurea receptors (SURs), a member of the ATP- binding cassette family of proteins. The pore-forming sub- unit Kir6.0 has two different members, Kir6.1 and Kir6.2, which share 70% amino acid identity. The regulatory sub- unit SUR is encoded by two distinct genes, SUR1 and SUR2, and is the site of action for antidiabetic drugs such as glibenclamide used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (Babenko et al. 1998 [1059]; Seino 1999 [1060]; Rodrigo and Standen 2005 [1041]; Ashcroft and Gribble 1998 [1062]).
Kir6.1 predicted AlphaFold size
Methodology for AlphaFold size prediction and disclaimer are available here
KATP channels - of which kKr6.1 is a key unit - are present on endomembranes, in particular in mitochondria (‘‘mitoKATP’’) (Inoue et al. 1991 [1057]; Paucek et al. 1992 [1058]).
Cell imaging showed that a major proportion of heterologously expressed Kir6.1-GFP and endogenously expressed Kir6.1 was distributed in the endoplasmic reticulum with little in the mitochondria or plasma membrane. (Ng [1056])
ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels - of which Kir6.1 is a central unit - are involved in a number of physiological and pathophysiological processes and form a link between cellular metabolism and membrane excitability. (Ng [1056])
Kir6.1 plays a role in modifying Ca2+ release from intracellular stores. (Ng [1056])
KATP channels -of which Kir6.1 is a key unit - are inhibited by increasing intracellular [ATP] and activated by increasing [ADP]. (Ng [1056])
The KATP channel opener diazoxide increased reactive oxygen species production, and glibenclamide abolished this effect. However, in cells lacking Kir6.1 or expressing siRNA or dominant negative constructs of Kir6.1, the same effect was seen. (Ng [1056])
References
Shyng S
et al.
Control of rectification and gating of cloned KATP channels by the Kir6.2 subunit.
J. Gen. Physiol.,
1997
Aug
, 110 (141-53).
Ashcroft FM
Adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels.
Annu. Rev. Neurosci.,
1988
, 11 (97-118).
Aguilar-Bryan L
et al.
Cloning of the beta cell high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion.
Science,
1995
Apr
21
, 268 (423-6).
Inagaki N
et al.
A family of sulfonylurea receptors determines the pharmacological properties of ATP-sensitive K+ channels.
Neuron,
1996
May
, 16 (1011-7).
Inagaki N
et al.
Reconstitution of IKATP: an inward rectifier subunit plus the sulfonylurea receptor.
Science,
1995
Nov
17
, 270 (1166-70).
Inagaki N
et al.
Cloning and functional characterization of a novel ATP-sensitive potassium channel ubiquitously expressed in rat tissues, including pancreatic islets, pituitary, skeletal muscle, and heart.
J. Biol. Chem.,
1995
Mar
17
, 270 (5691-4).
Tester DJ
et al.
Loss-of-Function Mutations in the KCNJ8-Encoded Kir6.1 KATP Channel and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome.
,
2011
Aug
11
, ().
Medeiros-Domingo A
et al.
Gain-of-Function Mutation, S422L, in the KCNJ8-Encoded Cardiac K ATP Channel Kir6.1 as a Pathogenic Substrate for J Wave Syndromes.
,
2010
Jun
14
, ().
Chen FR
et al.
[Effects of Guanxinkang on expressions of ATP-sensitive potassium channel subunits Kir6.1, Kir6.2, SUR2A and SUR2B in ischemic myocytes of rats].
Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao,
2010
May
, 8 (458-64).
Ng KE
et al.
The intracellular localization and function of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel subunit Kir6.1.
J. Membr. Biol.,
2010
Apr
, 234 (137-47).
Inoue I
et al.
ATP-sensitive K+ channel in the mitochondrial inner membrane.
Nature,
1991
Jul
18
, 352 (244-7).
Paucek P
et al.
Reconstitution and partial purification of the glibenclamide-sensitive, ATP-dependent K+ channel from rat liver and beef heart mitochondria.
J. Biol. Chem.,
1992
Dec
25
, 267 (26062-9).
Babenko AP
et al.
A view of sur/KIR6.X, KATP channels.
Annu. Rev. Physiol.,
1998
, 60 (667-87).
Seino S
ATP-sensitive potassium channels: a model of heteromultimeric potassium channel/receptor assemblies.
Annu. Rev. Physiol.,
1999
, 61 (337-62).
Ashcroft FM
et al.
Correlating structure and function in ATP-sensitive K+ channels.
Trends Neurosci.,
1998
Jul
, 21 (288-94).
Credits
To cite this page: [Contributors] Channelpedia https://channelpedia.epfl.ch/wikipages/53/ , accessed on 2026 Feb 23