Kv9.2
Description: potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 2 Gene: Kcns2 Alias: Kv9.2, kcns2
Kv9.2, encoded by HCNS2, is a member 2 of subfamily S of potassium voltage-gated delayed-rectifier channels. Kv9.2 is not functional by itself but can form heteromultimers with member 1 and with member 2 (and possibly other members) of the Shab-related subfamily of potassium voltage-gated channel proteins. NCBI [606]
Experimental data
Rat Kv9.2 gene in CHO host cells datasheet |
||
|
Click for details 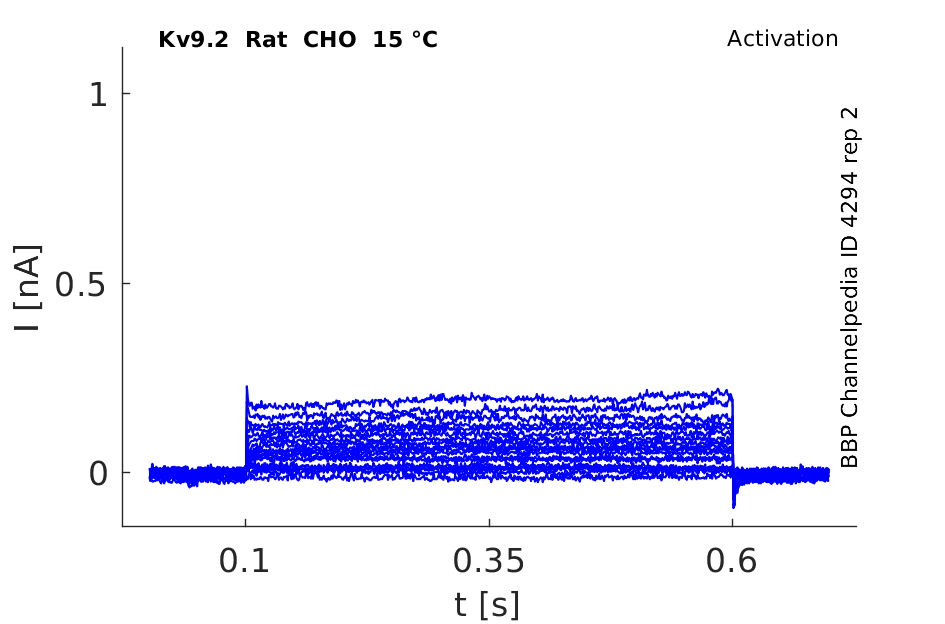
15 °Cshow 55 cells |
Click for details 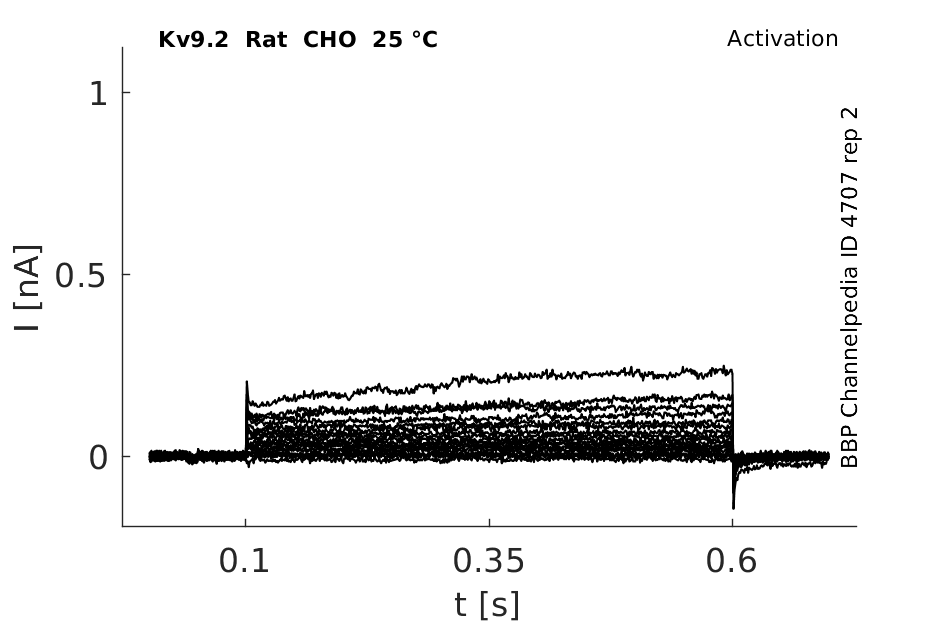
25 °Cshow 76 cells |
Click for details 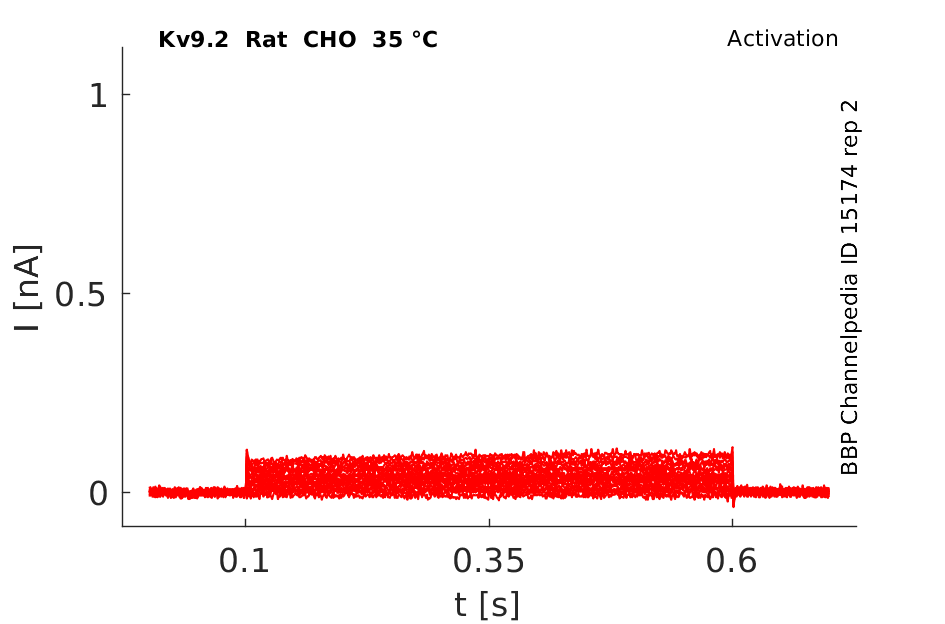
35 °Cshow 58 cells |
In contrast to the genes in the other subfamilies, members of the Kv8 and Kv9 subfamilies have been found to be incapable of forming functional channels when expressed either in oocytes or cell lines. Moreover, these mammalian genes appear to have no Drosophila homologs. [402]
Transcript
| Species | NCBI accession | Length (nt) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | NM_020697.4 | 5288 | |
| Mouse | NM_181317.4 | 5473 | |
| Rat | NM_023966.2 | 5476 |
Protein Isoforms
Isoforms
Post-Translational Modifications
Visual Representation of Kv9.2 Structure
Methodology for visual representation of structure available here
Structure of Kv9.2 ion Channel
The ORFs of Kv9.1 and Kv9.2 encode proteins of 497 and 477 amino acids, respectively, with a calculated molecular mass of 54.9 and 54.3 kDa (Fig. 1 A). Protein sequences reveal that all the structural characteristics of outward rectifier voltage-gated K+ channel α subunits (Kv) are conserved in Kv9.1 and Kv9.2, i.e. six putative transmembrane segments (S1 to S6), a transmembrane region (S4) showing five positively charged amino acids and a conserved pore-forming region (named H5 or P domain). As indicated in Fig. 1 A, Kv9.1 and Kv9.2 subunits contain several putative phosphorylation sites located in the cytoplasmic regions for protein kinase C, cAMP-dependent protein kinase, Ca2+-calmodulin kinase II, casein kinase II, and tyrosine kinase. No N-glycosylation sequence was detected [400]
Kv9.2 predicted AlphaFold size
Methodology for AlphaFold size prediction and disclaimer are available here
Kinetics of Kv9.2 with Kv2 Family

Kv9.2 Expressed Exclusively in the Brain
Northern blot analysis presented in Fig.2 shows that Kv9.1 and Kv9.2 mRNAs are expressed only in the brain. Specific probes detected two transcripts for Kv9.1 with an estimated size of 2.2 and 2.7 kb and one for Kv9.2 of approximately 5.3 kb. No expression was observed in heart, spleen, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, or testis [4000]
Inferior Colliculus
Kv9.1 and Kv9.2, two known members of the Kv9 subfamily, appear to be expressed diffusely in cells of the inferior colliculus [400].
Kv9.1 and Kv9.2 are neuronal modulatory alpha subunits that define a structural family designated as Kv9. They modulate Kv2.alpha subunits but have no functional activity by themselves. [400]. I.e., the kinetics of activation and the voltage-dependence of Kv2.1 currents are altered by such co-expression with Kv9.1 [402].
K+ channel functions are included in very diverse processes such as neuronal integration, cardiac pacemaking, muscle contraction, and hormone secretion in excitable cells [735], as well as in cell proliferation, cell volume regulation, and lymphocyte differentiation [736].
Kv2.1 and Kv2.2
Kv9.1 and Kv9.2 colocalized with Kv2.1 and/or Kv2.2 α subunits in several regions of the brain and alters the Kv2's kinetics as well [400]
References
Salinas M
et al.
New modulatory alpha subunits for mammalian Shab K+ channels.
J. Biol. Chem.,
1997
Sep
26
, 272 (24371-9).
Richardson FC
et al.
Modification of delayed rectifier potassium currents by the Kv9.1 potassium channel subunit.
Hear. Res.,
2000
Sep
, 147 (21-30).
Gutman GA
et al.
International Union of Pharmacology. LIII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of voltage-gated potassium channels.
Pharmacol. Rev.,
2005
Dec
, 57 (473-508).
Sheng M
et al.
Presynaptic A-current based on heteromultimeric K+ channels detected in vivo.
Nature,
1993
Sep
2
, 365 (72-5).
Wang H
et al.
Heteromultimeric K+ channels in terminal and juxtaparanodal regions of neurons.
Nature,
1993
Sep
2
, 365 (75-9).
Suh BC
et al.
Modulation of high-voltage activated Ca(2+) channels by membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate.
Neuron,
2010
Jul
29
, 67 (224-38).
Lewis RS
et al.
Potassium and calcium channels in lymphocytes.
Annu. Rev. Immunol.,
1995
, 13 (623-53).
Pongs O
Structure-function studies on the pore of potassium channels.
J. Membr. Biol.,
1993
Oct
, 136 (1-8).
Heginbotham L
et al.
Mutations in the K+ channel signature sequence.
Biophys. J.,
1994
Apr
, 66 (1061-7).
MacKinnon R
Pore loops: an emerging theme in ion channel structure.
Neuron,
1995
May
, 14 (889-92).
Pascual JM
et al.
K+ pore structure revealed by reporter cysteines at inner and outer surfaces.
Neuron,
1995
May
, 14 (1055-63).
Christie MJ
et al.
Heteropolymeric potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes from cloned subunits.
Neuron,
1990
Mar
, 4 (405-11).
Shahidullah M
et al.
Slow inactivation conserved in heteromultimeric voltage-dependent K+ channels between Shaker (Kv1) and Shaw (Kv3) subfamilies.
FEBS Lett.,
1995
Sep
11
, 371 (307-10).
Chen ML
et al.
Heteromultimeric interactions among K+ channel subunits from Shaker and eag families in Xenopus oocytes.
Neuron,
1996
Sep
, 17 (535-42).
Contributors: Rajnish Ranjan, Michael Schartner, Katherine Johnston
To cite this page: [Contributors] Channelpedia https://channelpedia.epfl.ch/wikipages/31/ , accessed on 2025 Dec 08